Note to Reader
This post is for educational purposes only. Always follow your institution’s guidelines and clinical best practices.
“I remember one time in an Ontario hospital, we were trialing our ‘brand new at the time’ Oxy2Pro mask in an Endoscopy suite for an upper GI procedural sedation when shortly after sedation, the EtCO2 waveform was all but lost, while the SpO2 reading remained at 100%. The Anesthetist noticed this discrepancy and attended to the patient, realizing they were apneic, with the patient’s head position dipping ‘chin to chest’. When mild stimulation of the patient didn’t resolve the apnea, the Anesthetist repositioned the head appropriately to open the airway to allow the Surgeon to continue scoping.
This corrective action restored the patient’s breathing, with pronounced EtCO2 waveforms returning, and the procedure was allowed to continue to completion. The Anesthetist commented to me afterward that it was the reliable performance of our Oxy2Pro, showing that there was in fact no EtCO2 waveform despite an SpO2 of 100%, that allowed him to act as quickly as he did, restoring breathing to the patient, keeping the patient from further decline, and ensuring the diagnostic Upper GI procedure was able to be finished.”
Every day, healthcare professionals rely on capnography to detect the smallest changes in patient breathing patterns. Yet many medical staff members still feel unsure about reading these valuable waveforms.
The truth about capnography is simple: it’s one of the most reliable tools we have for monitoring patient breathing. It shows us exactly how well a patient is breathing, in real-time, without waiting for other vital signs to change.
Capnography waves tell critical stories about patient health – stories that can make the difference between catching a problem early or facing an emergency.
This guide breaks down everything about capnography into clear, practical information.
I’ll cover the basics of how it works, show you how to read waveforms, and explain why it’s often more useful than pulse oximetry in many situations.
Whether you’re an experienced nurse looking to strengthen your skills or a new medical professional wanting to build confidence with patient monitoring, this guide will help you master capnography.
Let’s start with the fundamentals of how this vital tool works and why it matters in everyday patient care.
What is Capnography?
- Capnography measures carbon dioxide (CO2) levels in exhaled breath.
- It is crucial for assessing a patient’s ventilatory status in real-time.
- Vital in anesthesiology, intensive care, and emergency medicine.
Capnography Basics
Capnography is a vital monitoring tool in healthcare settings, measuring the concentration of carbon dioxide in a patient’s exhaled breath. This technology plays a crucial role in tracking patient ventilation, especially in critical care or surgery. It allows medical professionals to non-invasively assess a patient’s respiratory status in real-time by providing data on how effectively CO2 is being expelled by the lungs. The measured CO2 indicates how well a patient is ventilating and can signal respiratory problems like hypoventilation or hyperventilation before they become critical. One of the only other ways to measure a patient’s CO2 levels, would be to obtain a PaCO2 measurement through invasive arterial blood gases.
Understanding capnography begins with recognizing that it directly reflects the amount of CO2 expelled by the lungs. This makes capnography not just a tool for assessing ventilation but also a window into a patient’s circulatory and metabolic status. The data is displayed visually as a waveform called a capnogram, which shows the CO2 concentration throughout the respiratory cycle in real-time. Each part of this waveform provides insights into the patient’s respiratory function.
A capnograph is the device used to display this data. It consists of a sensor that detects CO2 levels and a monitor that visualizes these levels graphically. This setup allows for continuous, non-invasive monitoring, providing healthcare professionals with instant feedback on a patient’s ventilatory status. The key benefit here is the ability to make quick and informed decisions, particularly in critical care settings.
Types of Capnography
There are two primary types of capnography: mainstream and sidestream. Mainstream capnography involves placing a sensor directly within an intubated patient’s breathing circuit, typically close to the patient’s airway. This method provides a rapid response time and high accuracy in the measurement of CO2 but can be bulky since the sensor is in line with the patient’s airway.
Sidestream capnography, on the other hand, is typically used for spontaneously breathing patients and involves aspirating a small sample of the patient’s exhaled air and transporting it to a sensor located in the main monitoring unit. This method is more versatile and less intrusive, making it suitable for patients who might not tolerate additional in-line equipment. However, sidestream systems can have slightly slower response times and might be affected by moisture and secretions.
Benefits of Capnography Monitoring
- Fast response to respiratory changes.
- Better anesthesia management.
- Early detection of potential complications.
Enhanced Patient Safety
Real-time capnography offers vital information on a patient’s respiratory status. This can mean the difference between catching a respiratory issue early or missing critical warning signs. The ability to monitor carbon dioxide (CO2) levels continuously provides healthcare professionals with the data needed to make fast decisions.
Why can’t I just rely on the Pulse Oximeter?
Pulse oximeters can show when oxygen levels drop, but they don’t always correlate with the immediacy that capnography does. Capnography delivers immediate data on a patient’s ventilation status. This allows for prompt intervention. In cases like opioid-induced respiratory depression, the ability to act swiftly can prevent severe harm or even death.
Why can’t I just rely on the Pulse Oximeter to tell me how the patient is breathing? Because pulse oximetry doesn’t tell you how a patient is breathing, it is a reflection of the amount of oxygen being carried in the blood. And think about where we typically measure the % of O2 in the blood that a SpO2 reading provides; at the body’s extremities. When a patient stops breathing, their oxygen levels at their fingertips where the SpO2 probe is measuring doesn’t plummet immediately.
In fact, there are studies that show up to 60 seconds or more can pass between the cessation of breathing and a significant desaturation under 90% that would alert an HCP to a possible problem.* For that reason, pulse oximetry is considered a ‘lag indicator’ to a patient’s ventilatory status, making the ability to monitor with capnography all the more important.
Reduced Incidence of Adverse Events
Adverse events often happen without clear or timely warnings. Real-time monitoring through means like capnography can allow for faster detection of events, alerting caregivers more quickly, thereby improving the response time of HCP’s needed to reduce the potential harm or impact to the patient. This means the severity of adverse events is potentially significantly reduced – making the use of capnography safer for patients in procedures or those undergoing serial monitoring.
Improved Monitoring During Anesthesia
During surgery or procedural sedations, maintaining the right level of anesthesia is crucial. Capnography is key in balancing moderate or deeper anesthesia in spontaneously breathing patients. It helps anesthesiologists ensure patients are neither under- nor over-sedated, addressing both patient comfort and safety.
Maintaining Anesthesia Depth
Capnography monitors ventilation efficiency, which plays a significant role in determining anesthesia depth. If CO2 levels rise or fall unexpectedly, it might mean the anesthesia depth needs adjustment. This precise monitoring helps prevent complications such as hypoventilation.
Minimizing Hypoventilation Risks
Hypoventilation occurs when a patient breathes too slowly or too shallowly, leading to increased CO2 levels. It can lead to serious complications if not detected early. Capnography acts as a dependable indicator. It helps to mitigate these risks by providing real-time data, allowing clinicians to adjust ventilation as needed.
Optimizing Postoperative Care
Capnography isn’t only valuable during surgery; it’s also essential postoperatively. It ensures patients recovering from anesthesia are adequately ventilating, preventing issues like hypoxemia.
Continuous Monitoring Over Intermittent Checks
Continuous capnographic monitoring post-surgery can catch episodes of respiratory depression that periodic checks might miss.
Enhancing Patient Outcomes
Patient outcomes improve when issues are detected and addressed early. Maintaining continuous vigilance over ventilation through capnography improves recovery quality and shortens hospital stays by minimizing complications.
Supporting Emergency Situations
Beyond scheduled surgeries, capnography is instrumental in emergency medicine. It provides rapid feedback on a patient’s status during critical interventions like intubation or resuscitation.
Quick Validation of Intubation
In emergencies, ensuring that intubation is correctly placed is key. Capnography quickly verifies ET tube placement by assessing exhaled CO2 levels. This reduces the risk of catastrophic errors such as unrecognized esophageal intubation.
Effective Resuscitation
During resuscitation, capnography monitors the effectiveness of chest compressions and ventilation. It helps verify the return of spontaneous circulation, giving timely feedback to the medical team about the patient’s condition.
Tips on Interpreting Capnography Waveforms Effectively
- Break down complex waveform patterns for accurate diagnosis.
- Understand how different medical conditions alter waveform shapes.
- Learn from real-life cases to refine interpretation skills.
Understanding the Capnography Waveform
Capnography waveforms are essential in gauging ventilation status. They have distinct phases, each revealing specific aspects of a patient’s respiratory process, as outlined in various guides like those from Medtronic.
Key Features of the Waveform
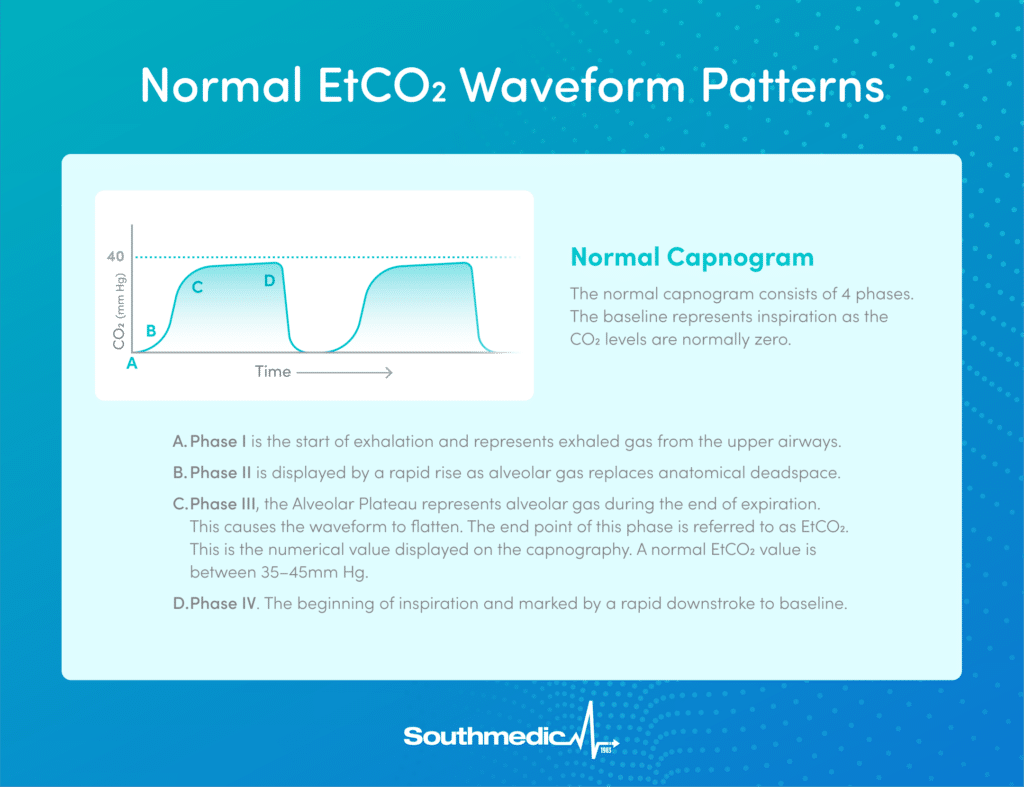
A normal waveform features four phases:
- Phase I: The line at the start is flat. It represents the time between inhalation and exhalation, which usually lacks CO2.
- Phase II: This phase shows the start of exhalation, where CO2 levels rise. This transition area from dead space to alveolar gas is marked by the alpha angle, which helps show how quickly CO2 peaks.
- Phase III: Known as the plateau, the CO2 level remains almost steady. The end of Phase III is typically where an EtCO2 value is measured and reported on the capnograph. The beta angle transition marks the start of the new breath.
- Phase IV: As inhalation begins again, CO2 falls, completing the cycle.
Normal capnograms resemble a shark-fin shape.
Waveforms offer a breath by breath analysis of a patient’s ventilatory status by measuring the concentration of exhaled carbon dioxide throughout the patient’s respiratory cycle. A patient’s normal PaCO2 as measured with an arterial blood gas (ABG) = 35-45mmHg. The end-tidal carbon dioxide (EtCO2) number that is measured at the end of exhalation is important, but EtCO2 is an estimate of PaCO2, and so practitioners shouldn’t expect EtCO2 measurements to equal PaCO2 readings you would get from an ABG. Just as important, if not more so, is the shape of the waveforms seen on the capnograph, and the repeatability / trendability that waveforms offer. A change in the real-time shape of a waveform can be a tip off to a change in the patient status, and so having a device that more accurately delivers waveforms to the capnograph is an invaluable monitoring tool.
Recognizing deviations like a flat EtCO2 or increased levels can highlight issues like airway problems or rebreathing see capnography tutorial for detailed exploration.
Common Patterns and Abnormalities
Understanding common waveform shapes allows for quick diagnosis:
- Flat EtCO2 Trace: Indicates serious issues like ventilator disconnection or airway problems.
- Increased EtCO2: Could mean reduced ventilation efficiency, often seen in cases like hypoventilation or bronchial intubation.
- Elevated Inspiratory Baseline: Often results from CO2 rebreathing or monitor contamination.
Experts stress the need to analyze waveform features such as rhythm and baseline height for diagnosing ventilator issues and troubleshooting, as noted by Infinium Medical.
Examples of Waveform Interpretation
Capnography Related Products to Include: Oxy2Mask EtCO2 and Oxy2Pro
Assessing capnography products requires looking at what each offers. You need patient device tools you can trust to sample EtCO2 effectively, at whatever oxygen flow rate is needed.
Oxy2Mask EtCO2
The Oxy2Mask EtCO2 is an innovative mask that combines advanced oxygenation capabilities with real-time capnography sampling. As an experienced respiratory therapist, I’ll break down how it works and the benefits in the context of patient safety and procedural convenience.
Simplified Use in Clinical Practice
The Oxy2Mask EtCO2 is “out of the bag ready,” meaning it’s easy to implement into your clinical workflow with minimal training. The integrated design can eliminate the need for separate EtCO2 sampling devices or other assembly requirements, reducing complexity and ensuring consistent performance.
By combining oxygen delivery and EtCO2 monitoring in a single device, the Oxy2Mask EtCO2 offers a comprehensive solution for improving patient safety and procedural efficiency for patients with potentially higher oxygen needs. This makes it a valuable addition to any respiratory therapist’s or anesthesiologist’s toolkit.
Why the Oxy2Mask EtCO2 Stands Out
- For Patients: It supports those with complex respiratory needs by providing high levels of oxygen while simultaneously tracking ventilatory status. This dual functionality reduces complications associated with sedation and improves overall safety.
- For Clinicians: It reduces the need for multiple devices, streamlines workflow, and enhances patient monitoring, especially in moderate to deep sedation scenarios.
Here are some of the benefits of Oxy2Mask EtCO2:
1. Advanced Oxygenation
The mask provides up to 83% FiO2 at 15 L/min, which is significantly higher than what traditional nasal cannulas or simple masks can deliver. This is critical for:
- Patients at risk for hypoxemia or airway compromise during sedation procedures.
- Situations where precise oxygen delivery is needed to prevent respiratory failure.
- An elevated FiO2 ceiling allows for an intraprocedural response to changing patient conditions, keeping the patient safe, and fewer interruptions to procedures.
2. Reliable and Efficient EtCO2 Monitoring
- Early Detection of Ventilatory Issues: By detecting changes in EtCO2 levels, the mask helps clinicians identify possible respiratory adverse events due to oversedation, airway obstructions, or apneas before they result in oxygen desaturation, improving patient outcomes.
- Workflow Integration: The mask’s design simplifies monitoring by integrating both oxygen delivery and EtCO2 sampling into a single device, without assembly, reducing setup time and enhancing efficiency.
- Versatile Detection: Whether your patient is a mouth or nasal breather, the patented diffuser can effectively pick up exhaled CO2 and sample it for continuous capnography monitoring.
3. Open Design for Procedural Access
For procedural physicians, the open design of the mask:
- Facilitates access to the oral cavity, which is particularly useful in dental or endoscopic procedures.
- Minimizes instrument interference, reducing the risk of equipment damage.
- Oxy2EtCO2‘s open design won’t trap exhaled CO2 in the mask, reducing the likelihood of CO2 rebreathing.
4. 360° Swivel Adapter
This feature enhances flexibility, especially in cases where patient positioning is complex or prone to shifting. It ensures:
- Continuous oxygen and EtCO2 delivery without interruption.
- Unobstructed procedural access for clinicians to get oxygen tubing and the sampling line out of line of sight.
Oxy2Pro
Designed to help you care for patients with higher O2 needs and/or undergoing longer procedural sedations, the Oxy2Pro Mask incorporates advanced EtCO2 sampling technology, ensuring exceptionally reliable readings even at higher oxygen flows. This enhances the clinician’s ability to make informed decisions and provide safer patient care.
I’ll break down how this mask addresses key challenges in oxygen therapy and why it’s a game-changer for clinicians and patients alike.
Meeting the Most Challenging Care Needs
The Oxy2Pro Mask addresses key challenges in clinical care by combining precise, elevated oxygen delivery with reliable EtCO2 monitoring, ensuring safer and more efficient patient management during sedation and respiratory support.
- Reliable EtCO2 Monitoring: Traditional methods often fail at higher oxygen flows or during mouth breathing, leading to inaccurate readings and potential misinterpretations. Oxy2Pro’s advanced EtCO2 sampling technology ensures consistent, accurate monitoring even under challenging conditions, supporting informed clinical decisions.
- Flexible Oxygen Titration: Unlike conventional systems, Oxy2Pro delivers oxygen concentrations from 5 to 15+ liters per minute, achieving up to 95% FiO2. This ensures tailored oxygen delivery, preventing hypoxemia and safeguarding patient outcomes during sedation procedures.
- Enhanced Procedural Access: With its innovative large membrane window, the Oxy2Pro provides superior access for scopes and tubes without compromising oxygenation or EtCO2 monitoring. This minimizes interruptions and ensures seamless procedures, reducing the risk of patient desaturation and escalating respiratory adverse events.
The Oxy2Pro Mask streamlines care, elevating safety and efficiency for both clinicians and patients in high-demand settings.
Why the Oxy2Pro Mask Stands Out
The Oxy2Pro Mask represents a significant improvement over traditional oxygen delivery systems by combining:
- Clinical Efficiency: Simplifies workflows and reduces time spent managing equipment.
- Safety and Efficacy: Ensuring reliable oxygen delivery to a higher ceiling with improved precision EtCO2 sampling, even at higher oxygen flows helps protect your patient.
- Intentional Solution: no more MacGyvered solutions to try to meet the needs of your patients under procedural sedation.
Key Benefits of the Oxy2Pro Mask
1. Clinician Flexibility and Efficiency
The Oxy2Pro Mask solves a persistent problem in care: the need to switch between multiple masks to achieve different oxygen concentrations. Here’s how it helps:
- Broad Oxygen Range: Its innovative design delivers effective oxygen therapy across a wide range of concentrations, putting patients less at risk for harmful respiratory adverse events intraprocedurally.
- Ease of Use: With Oxy2Pro being ‘out of the bag ready’, this eliminates the need for mask assembly, or frequent trips to restock masks, allowing clinicians more patient-focused time. Fewer interruptions mean fewer delays in patient care.
- Streamlined Workflow: With a higher FiO2 ceiling, and the ability to accurately track your patient’s ventilatory status with enhanced EtCO2 capture, clinicians are able to detect changes in their patient’s condition before they become threatening adverse events – not only keeping the patient safer, but also reducing intraprocedural interruptions, and seeing more procedures through to completion, allowing for diagnostic outcomes.
3. Enhanced Patient Safety
Safety is a critical component of any oxygen therapy device. The Oxy2Pro Mask ensures:
- Efficient Oxygen Delivery: Its diffuser technology organizes oxygen into focused vortices, directing it precisely to the patient’s nose and mouth. This improves oxygenation efficiency and ensures consistent delivery. Having elevated delivered FiO2‘s available minimizes patient risk in the middle of a procedure.
- Advanced EtCO2 sampling: Being able to capture EtCO2 tracings in our patented diffuser, even at higher oxygen flows, means the importance of capnography is preserved to help track your patient’s respiratory status throughout any procedural sedation
4. Intentional Solution
No more cutting holes in oxygen masks to fit scopes through, threading catheters under the mask or through the exhalation port to tape to the upper lip in hopes of procuring some sort of capnography tracing. Clinicians also don’t have to turn masks upside down, fitting uncomfortably on a patient’s face in order to gain oral access for the scope while having no idea how much oxygen they’re really delivering.
All these “MacGyvered” solutions are obsolete with an intentional solution that does it all: a higher oxygen ceiling at 95% FiO2 @ 15lpm, a technologically superior diffuser than can sample EtCO2 effectively, even at higher oxygen flows, and a star-shaped flexible window that allows easy access to safely advance and withdraw scopes through.
Conclusion
End-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring changes how healthcare professionals view patient monitoring. The knowledge you now have about capnography waveforms and clinical applications puts you ahead in providing better patient monitoring.
Capnography gives you real-time data about your patient’s ventilation status – information that can mean the difference between early intervention and delayed response. Whether you’re working in anesthesia, emergency medicine, or critical care, this tool adds a vital layer of patient safety.
Your next step is to practice interpreting waveforms in your clinical setting. Start with normal patterns, then build up to recognizing abnormal ones. Pay attention to how conditions like asthma and COPD affect the waveform shape. Connect with colleagues who regularly use capnography and learn from their experiences.
For more information on our Oxy2Mask line of open oxygen masks, contact us today.
citation: * = “Does EtCO2 monitoring during ED procedural sedation & analgesia with propofol decrease the incidence of hypoxic events?”; Miner, Chudnofsky et al.; 2009